AWS SageMaker - Empowering Your ML Lifecycle
In this post, I explore AWS Sagemaker’s features and use cases in Machine Learning. I am focusing on its capabilities that enable early deployment of Machine Learning models, significantly reducing time to production.
Introduction
Amazon SageMaker is a fully managed machine learning service that empowers data scientists and developers to swiftly build, train, and deploy machine learning models. With SageMaker, the process of building and training models becomes effortless as it eliminates the need for server setup or infrastructure management. The service provides an easy-to-use Jupyter notebook for seamless data exploration and analysis, capable of efficiently handling massive datasets.
What sets SageMaker apart is its flexibility, supporting custom algorithms and frameworks that can adapt to specific preferences and goals. Moreover, it offers two distinct interfaces: SageMaker Studio and SageMaker Console, which facilitate the management and execution of machine learning workflows
Use Case
One of the common challenges in the machine-learning world is
How to reduce the time to production for ML-driven solutions
A typical machine learning project begins with a Proof of Concept (POC) for a business use case. Usually, the POC is developed in notebooks like Jupyter or Colab, either locally or in private cloud accounts. Once promising outcomes are achieved in the POC, the team decides to transition the solution into production. However, this conversion phase from POC to Production often involves reworks in areas such as Data Engineering, Data Pipelines, and Model Evaluation, which inevitably increase the time required to reach production.
According to a study by Alegion and Dimensional Research, one-third of AI/ML projects encounter roadblocks and stall at the proof of concept phase.
The following graphics support the article’s analysis:
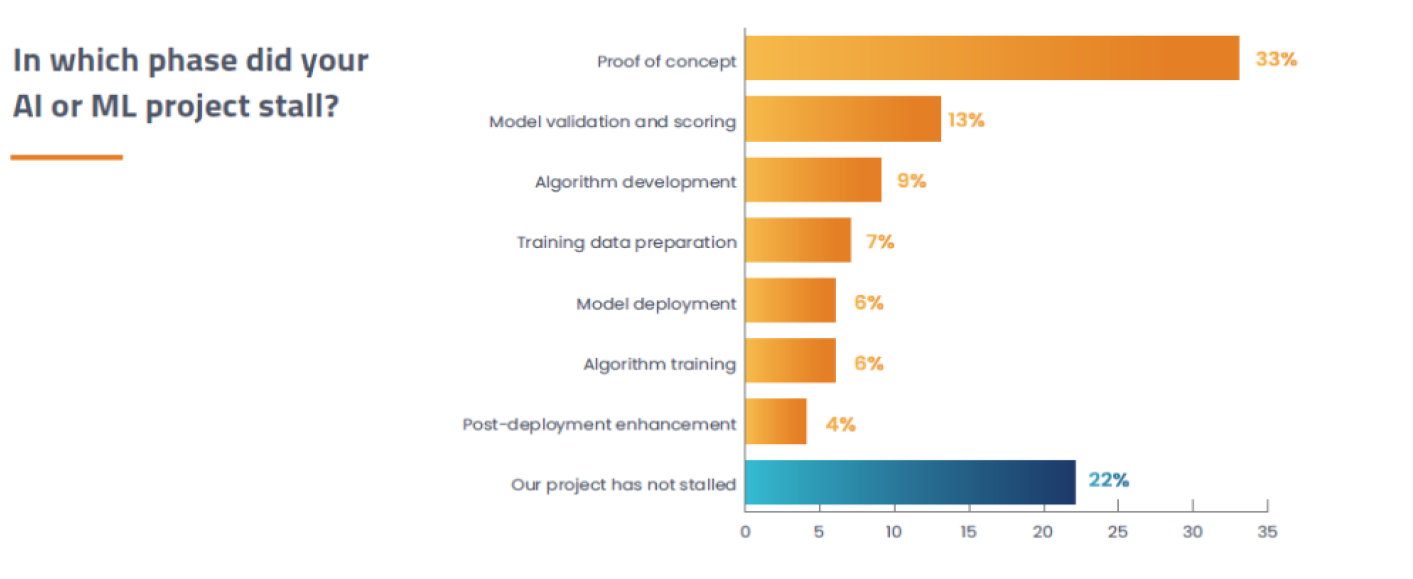
We can overcome these challenges by embracing the early adoption of AWS SageMaker.One of the standout features of SageMaker is its ability to streamline the deployment of models into a production-ready environment. By leveraging this comprehensive end-to-end machine learning cloud solution, Engineers and Teams can seamlessly experiment, build, train, and deploy ML models within a unified environment.
To illustrate this, I have created a Jupyter notebook where I have used SageMaker Studio to build, train, deploy, and monitor an XGBoost model. I have covered the entire Machine Learning workflow from feature engineering and model training to batch and live deployments for ML models. By utilizing SageMaker’s capabilities, I have tried to highlight how teams can efficiently navigate through the different stages of model development and deployment, accelerating the time to market.
Implementation
In the notebook you will discover how a single notebook instance allows us to accomplish the following tasks seamlessly :
- Downloading and processing the dataset stored in remote cloud storage (S3 bucket)
- Creating a SageMaker experiment to train the model
- Evaluating the model’s performance
- Deploying the model as RESTful HTTPS endpoints
- Monitoring the model
In SageMaker Studio notebooks are one-click Jupyter notebooks that contain everything you need to build and test your training scripts.
I have created a SageMaker Notebook, downloaded the dataset, and then upload the dataset to Amazon S3 bucket.After downloading and staging the dataset in S3 bucket, I created the SageMaker Experiment to train the model.
After training the model, I created offline/batch inference to evaluate model performance on unseen data. Evaluation metrics helped me to tune the model for better results.
With the help of SageMaker SDK libraries, I was able to deploy the best-performing model as a RESTful HTTP endpoint and monitor the deployed endpoints for any data drift.
All of this happened in a single notebook with the bare minimum code.
Features
As an end-to-end machine learning cloud solution, SageMaker comes with a plethora of features. However, here are a few standout features that are worth mentioning:
Infrastructure/Resource Management
Amazon SageMaker handles the management of an S3 bucket for storage and separate compute instances for processing. Processing tasks run on dedicated compute instances that are independent of the notebook instance. This allows for seamless experimentation and code execution in the notebook while processing is in progress. Upon completion of the processing job, SageMaker automatically terminates the instances, ensuring efficient resource utilization.
SageMaker’s ephemeral cluster approach means that each training job has its own dedicated EC2 instances, which are active for the duration of the training process. Development and training occur in separate EC2 instances, avoiding conflicts with virtual environments, package installations, and resource dependencies.
SageMaker also provides a notebook instance, which is an ML compute instance running the Jupyter notebook app. SageMaker handles the creation of instances and related resources, allowing you to use the notebook for data preparation and processing, code development, model training, deployment, testing, and validation.
Experiment Management
A SageMaker Experiment is a collection of processing and training jobs related to the same machine-learning project. It is a capability that lets you organize, track, compare, and evaluate your machine-learning experiments.
Each training job is logged as a trial within SageMaker, representing an iteration of the end-to-end training process. This includes pre-processing and post-processing tasks, datasets, and relevant metadata. With SageMaker’s experiment management capabilities, multiple trials can be included in a single experiment, making it easy to track and compare different iterations over time.
SageMaker Python SDK
SageMaker provides a Python library that simplifies model training and deployment. The library abstracts platform specifics, offering convenient methods and default parameters like deploy() and fit() for model deployment and training.
Sample Notebooks
SageMaker provides various Jupyter notebooks that demonstrate training and deployment of models using specific algorithms and datasets. You can start with a suitable notebook and modify it to accommodate your own data source and specific requirements.
Choices to train model
SageMaker offers flexibility in training your machine learning models. Here are a few options:
- Script Mode: SageMaker manages open-source containers such as
mxnet,TensorFlow,PyTorch,scikit-learn, and more. - Docker Containers: Bring Your Own (BYO) Model by using your own Docker file and managing user-specific Docker images and registry within ECR.
- AWS ML Marketplace: Access different algorithms and pre-trained model artifacts through a subscription model in the free tier, allowing for training your own data or using pretrained models.
- Built-in Algorithms: SageMaker provides a suite of algorithms, pre-trained models, and pre-built solution templates to quickly get started with training and deploying machine learning models.
Cost and Learning Curve
Amazon SageMaker offers a flexible and transparent pricing model that enables you to pay only for the resources you use. Data storage costs are based on the amount of data stored in Amazon S3 or other supported storage options. When it comes to training instances, you are charged for the compute resources utilized during model training.
AWS SageMaker provides a range of instance types with varying capabilities, and the pricing is dependent on factors such as instance type, duration of usage, and the number of instances employed.
Similarly, for model deployment, you are billed for the resources utilized to host your models in a production environment.
In my demo implementation, I utilized the ml.t3.medium notebook instance, which cost approximately 1.2 USD per day. While I paid a minimal amount for a demo or one-time activity, it is important to be mindful of SageMaker billing. In my experience, without proper cost optimization procedures, all cloud services can potentially result in high bills.
To effectively manage and optimize your costs with SageMaker, I recommend leveraging cost optimization features, including automatic model scaling and instance selection recommendations.
When it comes to learning, AWS offers extensive documentation, tutorials, and sample notebooks to facilitate the learning process. Furthermore, the availability of pre-built algorithms and optimized frameworks simplifies the implementation of machine learning models.
With its intuitive features, extensive libraries, and extensive community support, SageMaker helps reduce the learning curve. In many scenarios, ML Engineers don’t require advanced machine learning skills to access and leverage various ML functionalities in SageMaker
Last Word
AWS SageMaker offers a powerful end-to-end machine learning cloud solution, allowing engineers to seamlessly build, train, deploy, and monitor machine learning models within a single platform. By incorporating proper cost optimization techniques, SageMaker can prove to be a cost-efficient solution for organizations. While this post covers only a few standout features, there are many other capabilities to explore.
For further information, I recommend referring to the AWS Official Documentation for SageMaker and the Official SageMaker Deep Dive Tutorials Series by Emily Webber.
In competition with AWS SageMaker, Google and Microsoft also provide their own end-to-end machine learning cloud solutions. Google Cloud Datalab is a standalone serverless platform for building and training machine learning models. Meanwhile, Microsoft Azure Machine Learning Studio presents tough competition to SageMaker as Microsoft expands its services. Comparative studies suggest that SageMaker is the better option if you are well-versed in programming, especially for complex and large-scale projects. On the other hand, Azure Machine Learning Studio is more suitable for those with smaller and simpler goals.

Leave a comment